Media Player
This element is nestable, allowing for any Bricks elements to be added inside.
This element can be used inside query loops.
This element supports being used inside AJAX filtered content, either by Bricks’ native filter elements, WPGridbuilder, JetSmartFilters or PiotnetGrid
This element has it’s own interaction settings. Refer the interactions tab below for the list of element-specific triggers and/or actions.
This element support being used inside both components & nested components.
- General
- Quick Start
- Player UI
- Custom UI
- Chapters
- Accessibility
- Interactions
- Developer
- Support FAQ
This element provides you with a powerful media player, to play videos in Bricks with support for Bunny/Cloudflare stream, self-hosted mp4 (and other formats listed below). Use query loops for building custom playlists to feed to the player, add chapters, custom poster images, clip videos & visually build your own UI to best fit your site design.

View the demo page to get a quick idea of different setups / use cases. If you to set up a sandbox install based on that demo page, go here.
The element is powered by VidstackJS, the successor to Plyr/Vime.
Related elements for use with the player – Media Playlist, Media Control
Feature Highlights
- 4 Loading Options – Load only as the video comes into view (lazy loading), load only after user clicks the player or load only if video attempted to be played (built-in fallback to on-click where not supported) or custom if you want to control exactly when the media is allowed to load via interactions.
- Easily create your own playlist using Bricks’ query loop and the nestable ‘Media Playlist‘ element.
- Use local poster images.
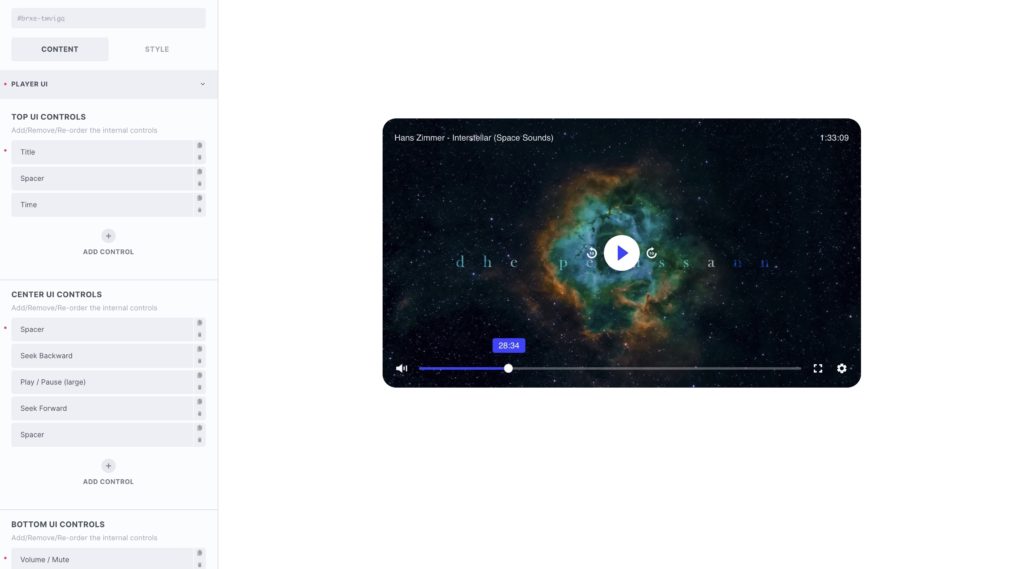
- Customizable UI. Add/remove/style/re-order all internal controls.
- Custom UI – Advanced option for nesting elements to create your own custom player UI.
- Divide media into skippable chapters via custom fields (or via TTF/SRT).
- Built-in support for using in filtered content (WPGB/Piotnet Grid/JetSmartFilters) and in lightboxes, modals.
- Built-in autopause (playing one player will automatically pause any others).
- Supports HLS (Bunny Stream, Cloudflare Stream etc)
- Add clip start/end times to videos.
- Auto-Generate Token Authentication for Bunny Stream (for setting expiry for video URLs)
Audio/Video Elements
There are two media player elements, one for video and one for audio.
Video – supports locally hosted video – mp4 & HLS video (URLs ending with m3u8, i.e., Bunny Stream, CloudFlare Stream) – Our recommendation is Bunny Stream.
(Note that Vimeo URL/embeds are not supported – if uploading videos to Vimeo, use the HLS link that is available & designed for use with custom players as part of Vimeo’s standard plan)
Audio – supports the following formats – m4a, m4b, mp4a, mpga, mp2, mp2a, mp3, m2a, m3a, wav, weba, aac, oga, spx.
Performance
By default, the media & the vidstackJS are lazy loaded i.e., gets added to the page once the user scrolls to the media player.
Media Loading
- Lazy (default) – The media will load only once the media player becomes visible (either scrolled to or revealed inside a popup/modal/lightbox)
- Click – The user needs to click the player (or a playlist item) for the media to load. Useful if displaying a notice where you want the user to click it before allowing playback. (Be mindful that with iFrame providers, iOS browsers require a click to play the video after the iFrame is added)
- Play – The user needs to click play for the media to load – For self-hosted videos, or HLS providers like BunnyStream. (will fallback to click for providers using iFrames)
- Custom – For when you need more control over when the media is able to load. For example, you may have a notice popup on your site, and when the user clicks it allows the media to load, or perhaps only once a form has been submitted then the user can play the video – either in one player or all players. (Bricks’ Interactions settings make this easy to set up)
UI Loading
As a further optimization when using the built-in UIs, there’s also a loading option.
- Lazy (default) – The player UI / controls are added to the DOM just before the player comes into view.
- Eager – Added immediately
For video hosting… for best performance & access to all player features, we recommend hosting videos via a CDN that supports HLS.. Bunny Stream, Cloudflare Stream, or Vimeo (only if using their HLS links – available on their standard plan).
Bunny Stream
Bunny Stream is a extremely affordable video hosting option, which will automatically create multiple versions of your video at different resolutions when the video is first uploaded and allows you to easily secure the video by only allowing the videos to be played from your specific domain. There’s also auto-generated captions for video.
Bunny Stream is also a great option for secure video playback as it has an additional CDN Token Authentication option for extra security. Ideal for membership sites where videos are restricted content and you don’t want users sharing the video URLs. More info on the advantages of using Bunny Stream for video hosting.

Enter your Token Authentication API key in BricksExtras settings to make sure unique tokens are generated in the media player for each user. This way, the video URLs will always expire after your chosen expiry time and won’t be usable outside of the situation where they need to be viewed on your site.

Cloudflare Stream
Videos hosted with Cloudflare Stream can also be used with the player, use the “HLS” option after uploading the video. (any video platform with HLS option can be used)
Cloudflare Stream will automatically create multiple versions of your video at different resolutions when the video is uploaded and allows you to easily secure the video by only allowing the videos to be played from your domain. It also has AI-generated captions that will automatically be picked up by the media player.

Auto-populate captions – for both Bunny Stream & Cloudflare Stream, the media player will now automatically populate any captions/subtitles associated with the video just from just that HLS URL and make them available in the player. This means if you’re using the AI auto-generate captions that come with both Bunny & Cloudflare when you upload a new video (or if you’ve added your own), you’ll only now need to add the URL for the video in the player and the captions will be available by default, no need to add anything else in the player settings. (API key for Bunny needed)
Auto detect site language (v1.5.7+) – If using multiple languages on your site (Polylang or similar), enabling this setting will detect which language the page is currently and prioritise the same language in the captions options (if captions for that language exist for the current media). This means the user can just simply toggle on the captions without having to find their language through the settings first.
Conditional Features
Some of the features, controls & settings in the player will be conditional, based on the browser support/settings, the current provider/source of the media, and what data is available for that media.
Some examples:
- If the site visitor has autoplay disabled in their browser, the player will detect it and won’t attempt to autoplay.
- If the current media doesn’t have any captions, both the caption toggle button control and the caption menu item inside of the settings menu won’t be visible. If using a playlist and the next media does have captions, then these will be made visible once that media is loaded in.
- If the current provider doesn’t support certain features, they won’t be seen in the player.
- If the device doesn’t support the FullScreen API, a fallback is provided to ensure the video plays full height/width in the browser window for that device (Plyr style). IOS will fallback to the native fullscreen player.
What the Media Player Is/Isn’t Useful For
There are lots of situations where video is used on websites, but where different solutions best suit.. so here’s a quick list to make it more clear where this media player could be the ideal solution and where it isn’t..
Useful for
- You want to be able to manage videos & playlists directly in WP (managing with video post types or repeater fields & using Bricks’ query loops to use) so the user can choose from a list of videos to play inside one player.
- You’re using a video delivery service such as Bunny Stream / Cloudflare Stream & don’t want to use their existing player, as you want more control over the style to better match your design.
- You generally need more control over the design/layout of your video player when wanting to display videos directly from the media library.
- Needing videos that only load only when visible, ie either when scrolled to or when a modal/lightbox opens up after the user has chosen to click to open.
- You need a player that can be used inside AJAX loaded content, for example inside AJAX popups or using Bricks’ filter elements where the content is being dynamically added/removed from the page without a page load (which will break most 3rd-party players).
Not Useful for
- Background videos – Having a custom player for this would be overkill; Bricks already includes background videos as a feature. Specifically, if no user interaction is needed and the video just needs to play in the background.. then often native HTML video elements or even just a looping GIF background-image is the cleanest solution.
- Allowing users to add custom players for videos inside posts. This is specifically a Bricks element, it’s not for wrapping embeds/mp4 videos that exist inside Gutenberg or other places around the site. It’s for adding to Bricks templates/pages & inside components where the content would be typically managed via custom fields.
- Any type of GSAP-type scrolling effect where a video is playing per frame as the user scrolls. For the same reason as the ‘background videos’ given above – often a simple video element to be controlled by your chosen scroll JS library will be the best solution, as no UI is needed & all playback is being controlled by the scroll JS anyway.
The media player comes with a lot of customization options, which can make it appear quite complicated. However, if you’re not trying to build something too custom and just need a nice-looking player to customize, it’s very quick to get started.
Here’s the quick start guide with how to first get set up and then to customize further if needed..
Minimal Setup
Set your media source – this is the URL of your video. If using a CDN to host the media (like Bunny stream, or Cloudflare Stream use the HLS URL ending with .m3u8)
Set a title (if needed) – it will be displayed wherever the ‘title’ control is inside the player (at the top by default).
That’s it. Now you have a fully functional media player. All commonly needed controls are in the default UI, with labels and optional tooltips in place. Any external connections to third party are lazyloaded by default.
Customize
Make some customizations to the player and controls..
Changes to the UI – You may prefer to switch a few controls around, maybe add a large play button in the center. Maybe add some ‘skip forward’, ‘skip back’ buttons. This can all be done from the ‘Customize UI’ tab. Change the order, add/delete different controls for each zone, and customize each icon/label if needed.
Player styles – The player itself and controls can be styled from the ‘General styling’ tab. Here you can add global styles that will apply to all controls of the same type (styling using a class if you want to apply these styles to multiple players across your site). Change colors, icon sizes, button padding, gaps between the controls, etc. Volume slider, time slider, and captions all have their style options.
Now you have your custom player, styled to fit better with your overall site design.
Optimize
Configure the behavior of the player and add more content..
Load strategy – By default, the player won’t load any media until the media player is scrolled to (lazy loaded). You may want to completely prevent any media loading unless the user interacts with the player. In this case, choose ‘on click’ as the load strategy and set up a local poster image to show where the video would be. The player UI and the image will show, and then as the user clicks the media will load. (note if using traditional iframe providers on some browsers this will mean the user will need to click again to then play the player after the media has loaded due to play restrictions – iOS specifically)
Config / Behaviour – Make tweaks to the overall behavior of the player based on the use case. Choose to pause the video when out of view, aspect ratio, how long the controls take to hide after the user starts watching etc..
Add subtitles/captions/chapters – Chapters are great for dividing up the content and allowing users to skim through multiple topics.
Advanced
When you need something more custom..
Custom UI – Sometimes you just need a completely different layout, the custom UI option removes the default UI completely and gives you a blank canvas. Fill the player with media controls and any other elements.
Set up Playlists – If you have multiple videos that you want the user to have access to, an alternative to adding lots of players is to instead set up one player and add a playlist.
Out of the box, the built-in UI comes with two nice, minimalistic layouts with the common controls. These can all be customised, repositioned, use custom icons, etc.
The UI is divided into three ‘zones’, positioned at the top, center and bottom of the player. There’s also optional full width time-slider below the bottom controls for Layout 1, and below the controls for the Layout 2 (optional because you can also include a time slider as one of the controls inside any of the other zones).
The player controls (see full list below) can be added/removed/re-ordered to create your layout. These controls will fade away once the user starts watching the video. Note that some of these controls are conditional and will only be visible based on if they are available for the current media being played.
Layout 1
Minimalist layout.

Default Controls:
Top zone – volume, full screen & settings menu.
Middle zone – large play button.
Bottom Zone – media title and full-width time slider below.
Layout 2
YouTube-esque type layout with controls underneath the time slider.

Default controls:
Top zone – media title.
Middle zone – none.
Bottom Zone – play, volume, time, fullscreen, settings menu with full-width time slider above.
Audio Player
When the media player is set to audio player, it has the same customisation options and controls, but just starts with a slightly different default configuration more suited to audio (see image below). The same three zones top/center/button are available for being able to stack layers of controls on top of each other if needed (custom nestable UI also supported)
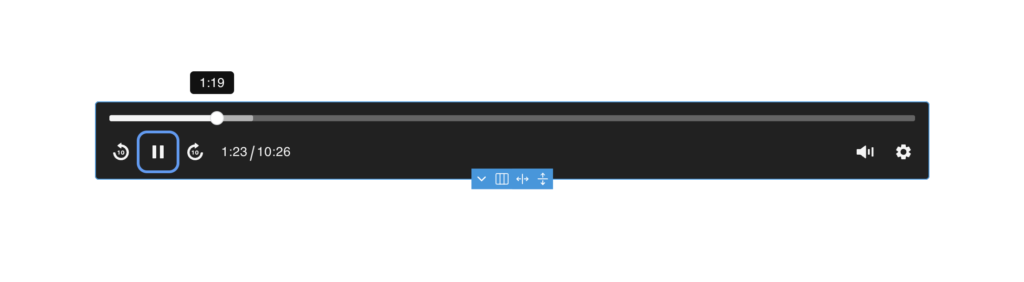
Default controls:
Top zone – none.
Middle zone – none.
Bottom Zone – seek backward, play, seek forward, volume, time, settings menu with full-width time slider above.
Control Visibility
Each zone and each control comes with some visibility options to allow for customising the player UI based on the current state of the player. ie if the player has loaded the media, or if the player has been played.
For example, if choosing not to load the media until a user actually clicks the player (via the loading settings), you may wish to only reveal part of the UI until the player has been clicked and the media has been loaded in..
Player Control Types
Note that any controls with an asterisk next to their name in the dropdown are displayed conditionally. For example, if there are no chapters for the current video in the player, neither the chapter menu button nor the chapter title elements will appear.
‘Play’ – Play/pause playback
‘Play (Large)’ – A larger play/pause playback
‘Seek-forward’ – Fast forward by the seek time (default 10 seconds)
‘Seek-backward’ – Rewind by the seek time (default 10 seconds)
‘Time slider’ – The progress bar and scrubber for playback and buffering
‘Time’ – For showing the current time of playback & The full duration of the media
‘Title *’ – The title of the current media, either coming from the title settings or dynamically from the video source.
‘Mute’ – Toggle mute – with an optional volume slider.
‘Captions *’ – Toggle captions on/off (if they exist)
‘Chapter Menu *’ – Open up the chapter menu
‘Chapters Title *’ – Display the current chapter (will change as the media goes through different chapters)
‘Settings’ – Settings menu with conditional options for speed, audio, quality, accessibility options
‘Fullscreen *’ – Toggle fullscreen (video only)
‘Spacer’ – The spacer control is to easily add the gap between the controls to allow for, for quickly aligning left/right.
‘Custom text’ – Add your own text
‘Image’ – Add your own image (ideal for if needing to add branding to the UI)
‘Poster image *’ – Display poster image for current media
‘Previous item’ – Button to skip to the previous item in the playlist
‘Next item’ – Button to skip to the next item in the playlist
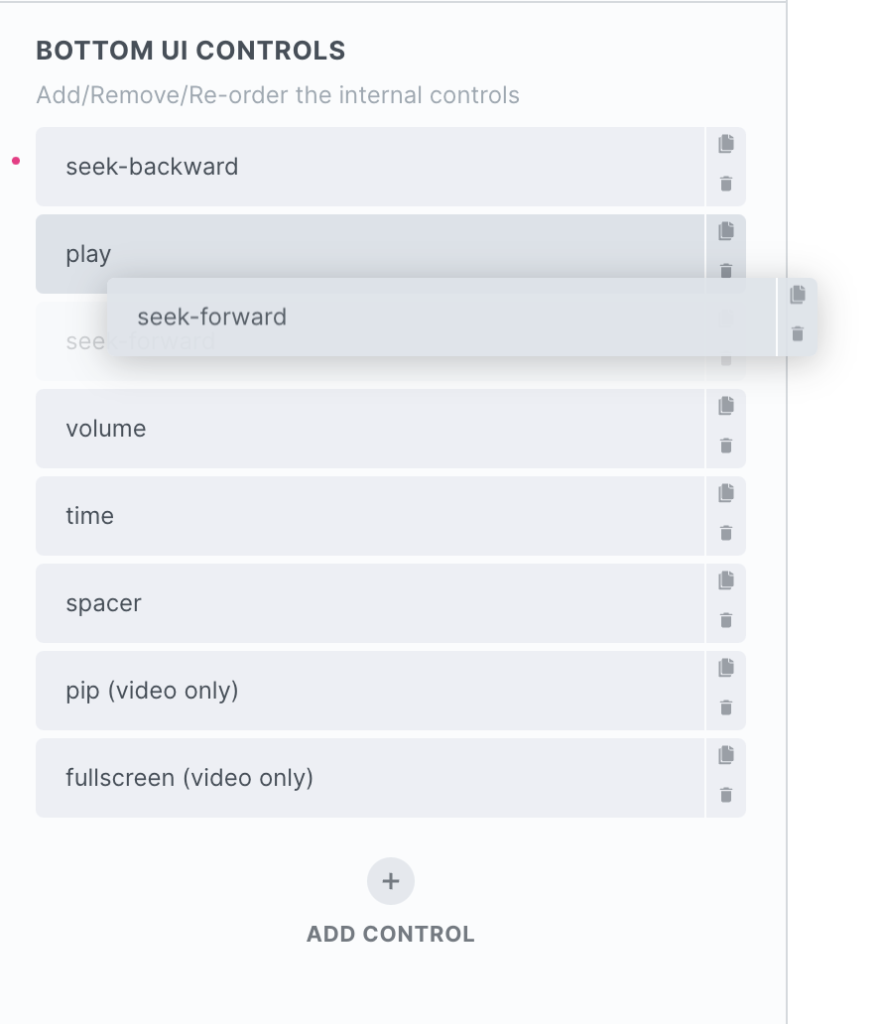
Each control has it’s own individual settings and can be arranged in any order within the UI zones.
Icons
All the icons can be changed to use your own custom icons from Bricks. If you like the default UI style, and want to find more icons with that same style you can find the icon pack here that we’re using, where SVGs are available for download.
Settings Menu Control
The ‘settings’ control (with the default cog icon) opens up a list of settings when clicked that will be unique to the current media in the player.
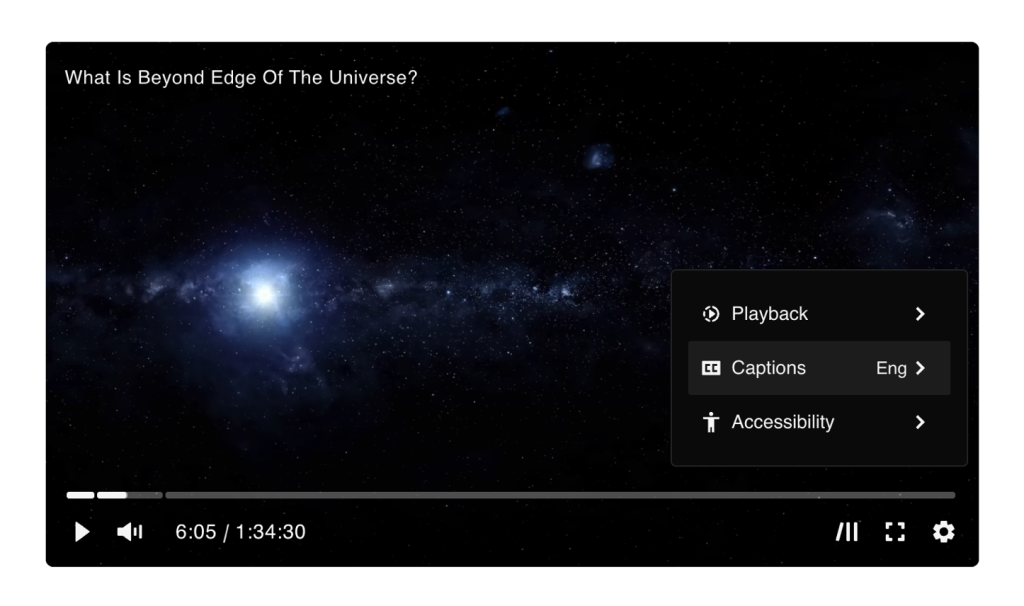
These menu items are added dynamically as they become available, depending on the media playing. For example, if there are no chapters or captions, these menu items won’t be added.
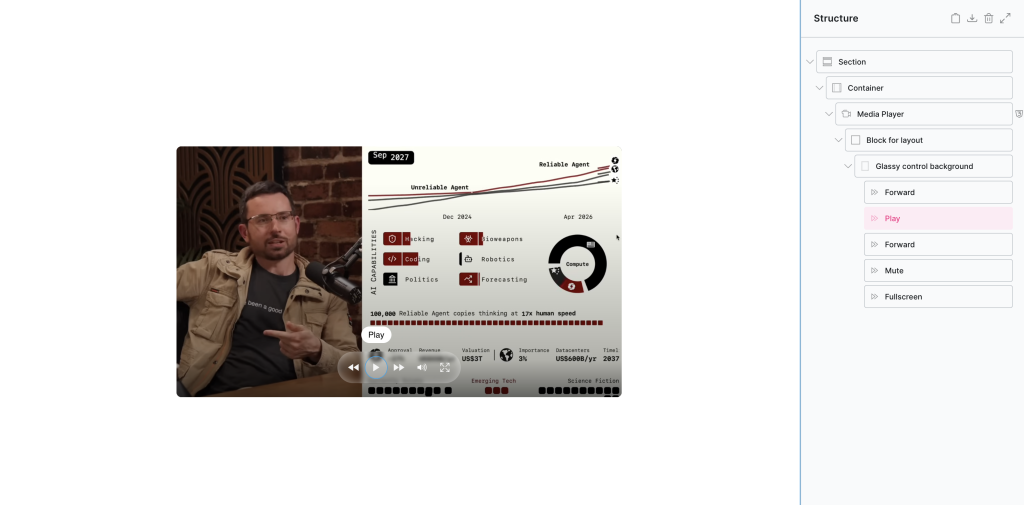
Custom UI (advanced)
The built-in UI has enough customisation options to cover most use cases for video players. Most common UI layouts can be achieved from those settings alone, quite quickly by moving the settings around to where you need them and styling the buttons. All the controls can be customised, styled, change icons, and positioned around the top,center and bottom of the player.
To cover the other use cases, (for users needing create custom UIs) there’s also an option to completely remove the built-in UI and build your own by nesting in active controls, or any elements, where you need them.
As with the controls built into the player, these can be customised, styled, icons changed, tooltips added etc. The main difference here is that you’re in 100% control of the inner layout using the Bricks flex/grid and whatever custom positioning & styling you need for each indivdual part.
For details on adding active controls inside your player layout, see the Media Control element.
Example custom layout.. (notice the layouts are created using ‘block’ elements using flex/grid. Neither the controls or the player itelf is controlling the layout, it’s all being done with Bricks like any other layout of elements)
The above are just examples, with custom UI the layout/styling would be entirely up to you.
Note that the custom UI should be considered an ‘advanced option’, if you’re just looking for something to add a video to a page and style to match your site, this option is likely overkill. Although it gives maximum flexibility, building a player UI with considerations for all the different device sizes, and player states is no small feat and may take a while to get right if you haven’t done it before.
Adding chapters to media is a great way to split up longer content. After adding chapters, three things in the media player will change.
- The ‘time slider’ control will be divided up into chapters with the chapter title in the tooltip as the user scrubs through the timeline.
- The ‘title’ control will auto-update as the player reaches each chapter time.
- The ‘settings’ control will include any chapters to allow users to skip through each chapter.
There are three ways to add chapters to your media player..
Text Tracks
If you already have a VTT file or SRT, simply add as a new text track as you would if adding subtitles or captions. (more about the WebVTT format)
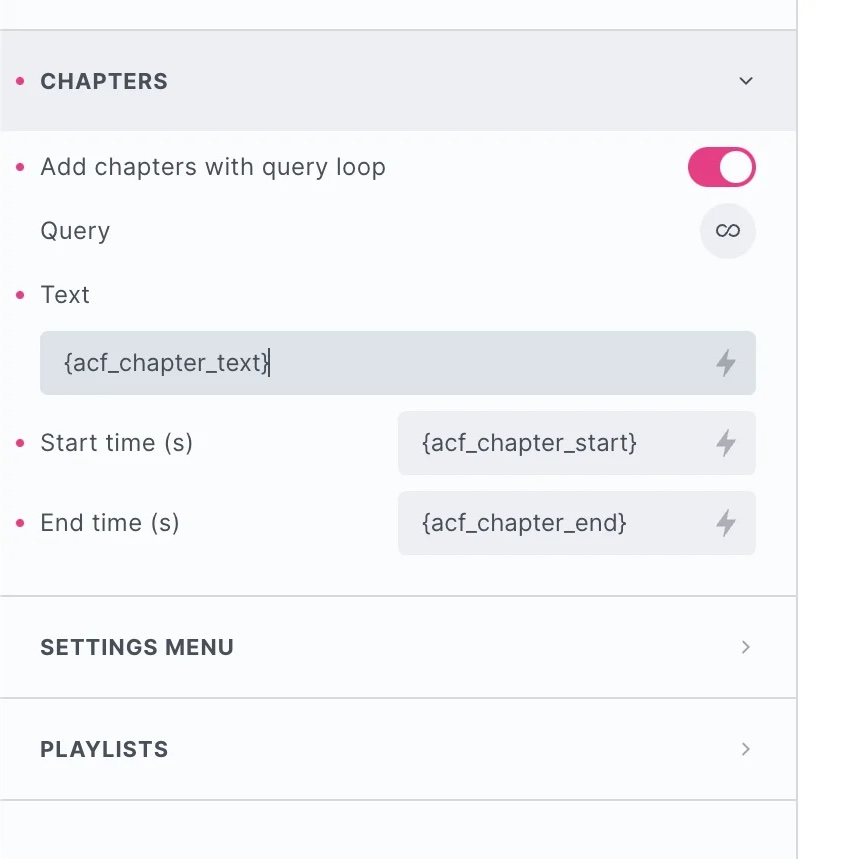
Adding chapters via settings
If you prefer to add the chapter data inside Bricks, head to the ‘chapters’ tab and either in the data for each chapter there.

Query Loop / Dynamic data
Or select the query loop option and set up a query for populating the chapters dynamically with custom fields.
Thumbnails – If hosting your videos with a provider that creates preview thumbnails (such as Mux), enter the VTT file or story board JSON to display preview thumbnails.
Keyboard Interaction
(To control whether these keys control the player globally, or only when that particular player is focused, go to Media Player > Interaction > Keyboard)
| Key | Action |
|---|---|
0 to 9 |
Seek from 0 to 90% respectively |
space |
Toggle playback |
K |
Toggle playback |
| ← | Seek backward by the seekTime option |
| → | Seek forward by the seekTime option |
| ↑ | Increase volume |
| ↓ | Decrease volume |
M |
Toggle mute |
F |
Toggle fullscreen |
C |
Toggle captions |
L |
Toggle loop |
Note that ‘Element Interactions’ must be enabled in BricksExtras > Misc settings.
This element adds new triggers to Bricks’ interactions options, so you can trigger actions based on the state of the element.
Triggers
Started – Triggered the moment the media is first played.
Ended – Triggered when the media reaches the end.
Paused – Triggered when user pauses the player.
Resumed – Triggered when user resumes playback after the player had been paused.
Seeked to new time – Triggered when user finishes using the time slider to seek to a new time.
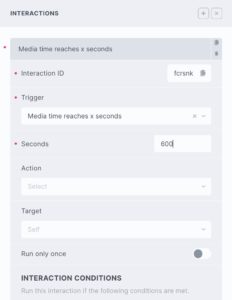
Time reaches x from start – Triggered the first time the media reaches x from the start. (x can be a fixed time in min/sec or a percentage of the duration)
Time reaches x from end – Triggered the first time the media reaches x from the end. (x can be fixed time in min/sec or a percentage of the duration)
Watch time has reached x – Triggered after the user has played at least x (x can be fixed time in min/sec or a percentage of the duration).
Options
Time measurement – For the time based triggers, it allows you to choose between a fixed time (in minuted/seconds) or a percentage based time (ie 5% from the end of the video)
Allow action if player in fullscreen? – Choose whether to trigger the action when the user is currently watching in fullscreen (ie isn’t viewing the browser window)
– True – Will trigger the action (useful if you’re using a trigger to display something within the player or to control the player)
– False – Will disable the action if currently in fullscreen mode.
– Wait – Will wait until the user has finished in fullscreen mode and then run any action that was set up.
– Force Exit – When it triggers, it will force the video out of fullscreen mode and run the action.
Trigger Delay (ms) – Allows you to set a short delay between the actions.
Actions
The element can be controlled with interactions.
- Set the target to the element using a CSS selector
- Use one of the following functions below to set the action.
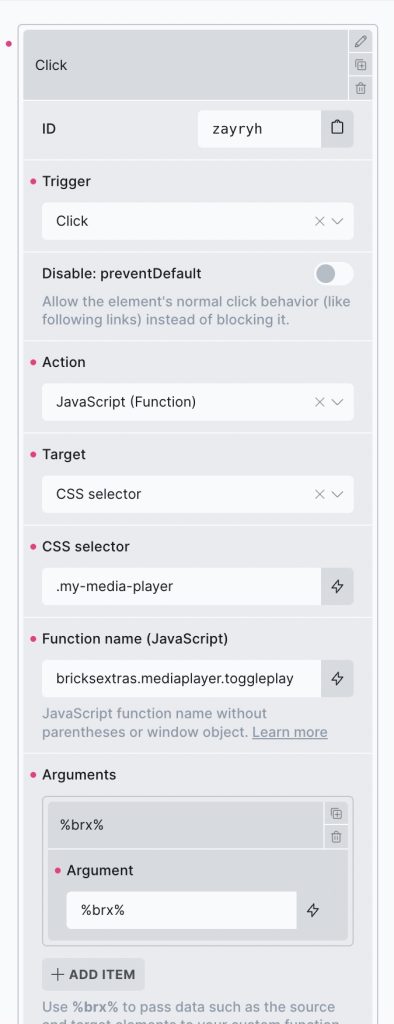
(always add the %brx% as the argument, which is required for Bricks interactions whenever using the JS action)
bricksextras.mediaplayer.play – Start playback
bricksextras.mediaplayer.pause – Pause playback
bricksextras.mediaplayer.toggleplay – Toggle between play/pause
bricksextras.mediaplayer.togglemute – Mute or disable mute
bricksextras.mediaplayer.enterfullscreen – Enter full screen mode (if supported)
bricksextras.mediaplayer.exitfullscreen – Exit full screen mode (if supported)
bricksextras.mediaplayer.skip – Skips the media to the new time (second parameter for seconds)
bricksextras.mediaplayer.load – Ideal if using custom loading strategy on the player. Will load the media for any players matching the given selector. Add a second parameter to ‘true’ if you wish for this to be remembered in the browser local storage, so on next page load the media will automatically load. The main use case is that you need the user to agree to something, so they click to load the players. When the same visit returns, ideally you don’t want them to have to click again.
You can easily control the media player programmatically in your JS, first you need to get the instance. (find the data-x-id attribute on the element for the identifier for that player)
Example code.. (if the element data-x-id was ‘xkjsjd’)
First, get the instance..
const mediaPlayer = xMediaPlayer.Instances.xkjsjd
Controlling the player and listening for state changes..
/* play */
mediaPlayer.play()
/* pause */
mediaPlayer.pause()
/* go full screen */
mediaPlayer.enterFullscreen()
/* EVENTS */
mediaPlayer.addEventListener('ended', () => {
/* do something when video reaches end */
})
mediaPlayer.addEventListener('paused', () => {
/* do something when video is paused */
})
mediaPlayer.addEventListener('play', () => {
/* do something when video starts to play */
})
/* open modal element when user reaches 60 seconds into video play */
mediaPlayer.addEventListener('time-update', () => {
let seconds = 60;
if (seconds === Math.floor( player.currentTime ) ) {
xOpenModal( 'modal-1' )
}
});Player Status Data Attributes
For more dynamic style options, based on the state of the player, see the following list of data attributes that are added/removed from the player as it changes it different states. If you need to show/hide controls or other elements conditionally based on certain states of the player, these attributes make that easy to do.
|
data-autoplay |
Autoplay has successfully started. |
|
data-autoplay-error |
Autoplay has failed to start. |
|
data-buffering |
Media is not ready for playback or waiting for more data. |
|
data-can-fullscreen |
Fullscreen mode is available. |
|
data-can-load |
Media can now begin loading. |
|
data-can-pip |
Picture-in-Picture mode is available. |
|
data-can-play |
Media is ready for playback. |
|
data-can-seek |
Seeking operations are permitted. |
|
data-captions |
Captions are available and visible. |
|
data-controls |
Controls are visible. |
|
data-ended |
Playback has ended. |
|
data-error |
Issue with media loading/playback. |
|
data-fullscreen |
Fullscreen mode is active. |
|
data-ios-controls |
iOS controls are visible. |
|
data-loop |
Media is set to replay on end. |
|
data-media-type |
Current media type (audio/video). |
|
data-muted |
Whether volume is muted (0). |
|
data-orientation |
Current screen orientation (landscape/portrait). |
|
data-paused |
Whether playback is paused. |
|
data-pip |
Picture-in-picture mode is active. |
|
data-playing |
Playback is active. |
|
data-playsinline |
Media should play inline by default (iOS). |
|
data-pointer |
The user’s pointer device type (coarse/fine). |
|
data-preview |
The user is interacting with the time slider. |
| data-seeking | User is seeking to a new playback position. |
|
data-started |
Media playback has started. |
|
data-view-type |
Current view type (audio/video). |
|
data-waiting |
Media is waiting for more data to resume playback. |
|
data-focus |
Whether player is being keyboard focused. |
|
data-hocus |
Whether player is being keyboard focused or hovered over. |
|
data-x-wait |
Whether player is waiting for source change. |
Example Uses
- You may have a vertical video, where you decide you want to change the player background to black if the user choosing to watch the video full screen.
- You decide to hide the time slider when the video is full screen.
Using the attributes above, these types of changes can be made with just a couple of lines of CSS.
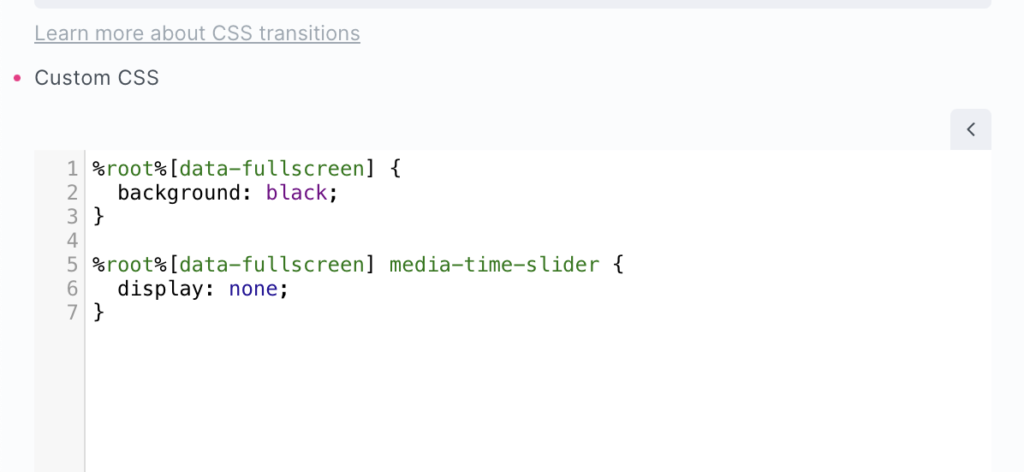
Familarising yourself with the above data attributes and the controls will allow for lot of customisation outside what is available in the settings.
Vidstack
For further customisation of behaviours, refer to the Vidstack API documentation